By Writer Content
Nepal Bank Limited (NBL): Addressing the Downward Trends in EPS, NPL, Net Worth, ROE, and Distributable Profit

EPS Decline in Nepal Bank Limited (NBL) Reflects Banking Sector Challenges
Nepal Bank Limited (NBL), a prominent institution in the banking sector, has reported a significant decline in its Basic Earnings Per Share (EPS) over the past five years. The latest data for the third quarter of the fiscal year 2080/2081 shows an alarming drop to Rs. 1.18, compared to Rs. 16.17 in the same quarter last year. This steep decrease marks a worrying trend for NBL and raises questions about the underlying challenges facing the banking sector.
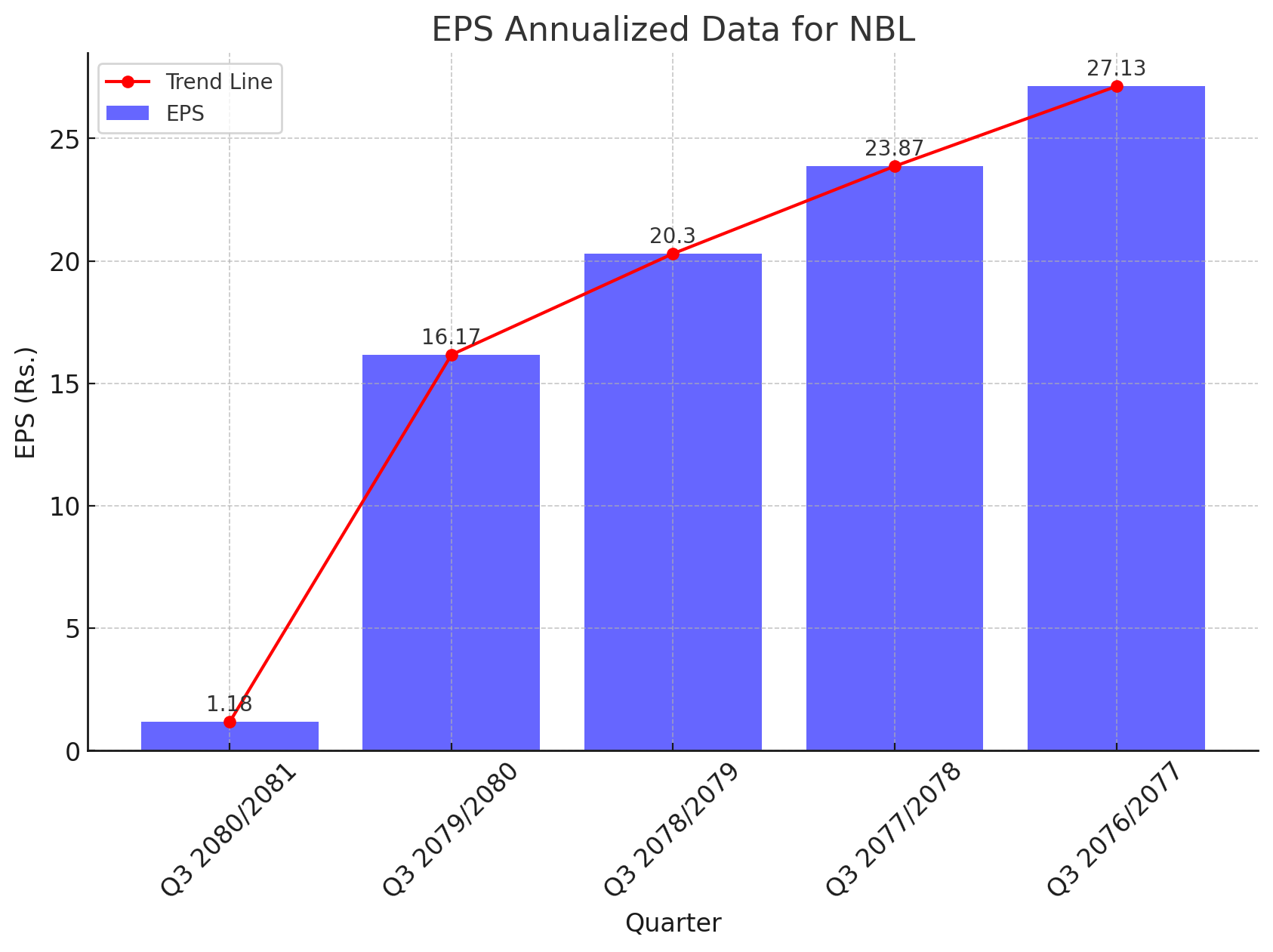
Historical EPS Performance:
Q3 2080/2081: Rs. 1.18
Q3 2079/2080: Rs. 16.17
Q3 2078/2079: Rs. 20.3
Q3 2077/2078: Rs. 23.87
Q3 2076/2077: Rs. 27.13
The consistent decline in EPS from Rs. 27.13 in Q3 2076/2077 to Rs. 1.18 in Q3 2080/2081 highlights a significant erosion in the bank's profitability. This trend is indicative of the broader challenges within the banking sector, including increased competition, regulatory pressures, and economic uncertainties.
Interpretation:
The sharp decline in EPS can be attributed to several factors:
Economic Slowdown: The overall economic slowdown has impacted the banking sector's growth, leading to reduced lending opportunities and lower interest margins.
Increased Competition: The entry of new players in the banking sector has intensified competition, squeezing profit margins for established banks like NBL.
Regulatory Changes: Stricter regulatory requirements have increased compliance costs, further impacting profitability.
Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): Rising NPAs have forced banks to make higher provisions, affecting their bottom line.
The significant drop in EPS this year is a cause for concern and calls for strategic measures to revitalize the bank's performance. NBL needs to focus on enhancing its operational efficiency, diversifying its product offerings, and leveraging technology to improve customer experience and reduce costs.
Strategic Actions for Recovery
To address these challenges and reverse the declining trend, NBL must consider the following strategic actions:
Cost Optimization: Implementing cost-cutting measures and optimizing operational processes to improve efficiency.
Digital Transformation: Investing in digital banking solutions to enhance customer service and expand market reach.
Risk Management: Strengthening risk management practices to reduce the incidence of NPAs and improve asset quality.
Market Diversification: Exploring new markets and revenue streams to mitigate the impact of economic downturns.
Conclusion
The decline in NBL's EPS underscores the need for urgent intervention and strategic realignment. While the challenges are formidable, proactive measures and a focus on innovation can help NBL navigate this difficult period and emerge stronger. The bank's leadership must prioritize sustainable growth strategies to restore investor confidence and ensure long-term profitability.
Rising Non-Performing Loans: A Growing Concern for Nepal Bank Limited (NBL)
Nepal Bank Limited (NBL) has experienced a concerning rise in its Non-Performing Loans (NPL) ratio over the past five years. The NPL ratio, which indicates the percentage of loans that are in default or close to being in default, has shown an upward trend, reflecting increasing challenges in loan recovery for the bank.
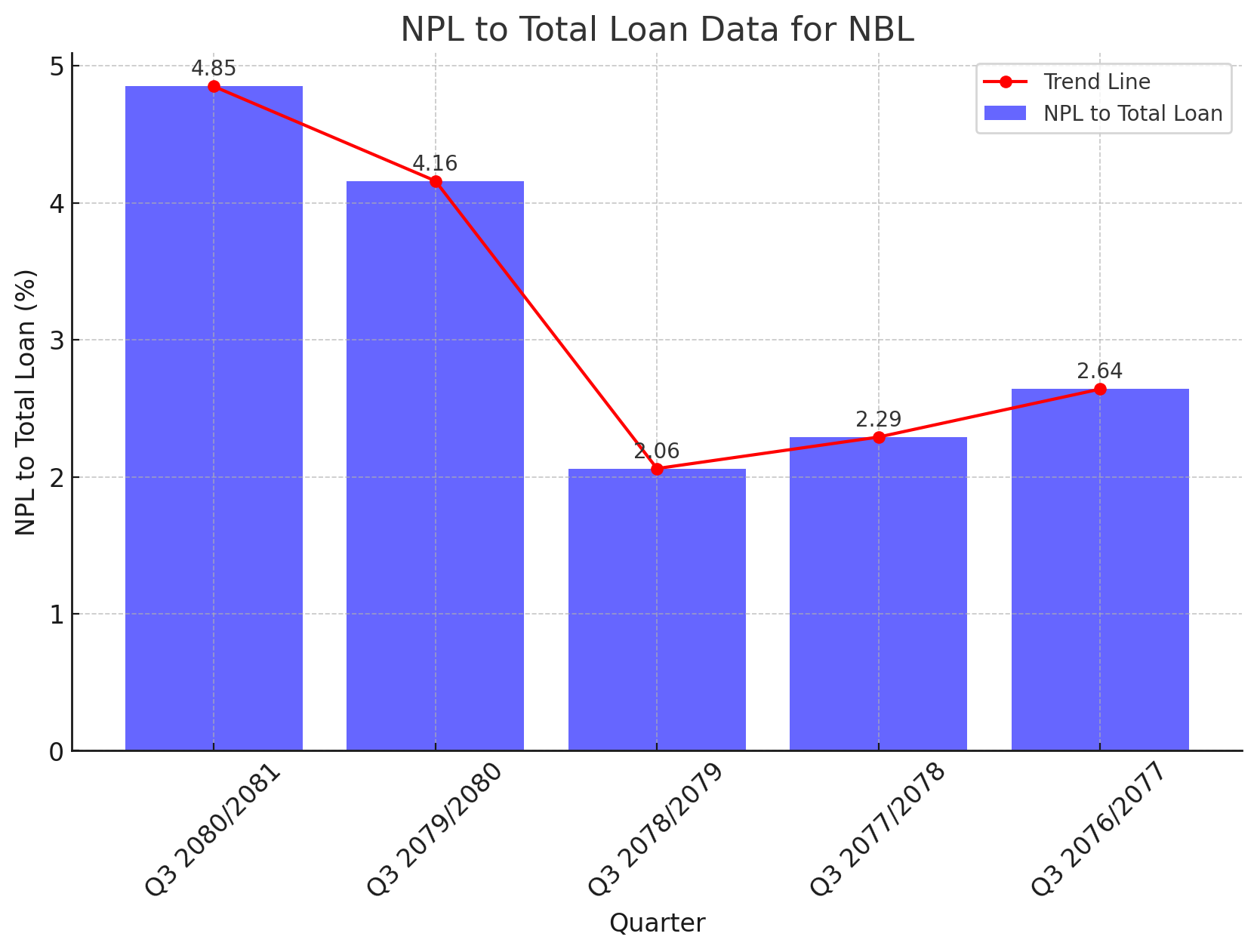
Historical NPL to Total Loan Ratio:
Q3 2080/2081: 4.85%
Q3 2079/2080: 4.16%
Q3 2078/2079: 2.06%
Q3 2077/2078: 2.29%
Q3 2076/2077: 2.64%
Interpretation:
The significant increase in the NPL ratio from 2.06% in Q3 2078/2079 to 4.85% in Q3 2080/2081 is alarming and suggests deteriorating asset quality. Several factors can be attributed to this trend:
Economic Slowdown: An overall economic downturn can lead to financial distress among borrowers, resulting in a higher number of loan defaults.
Poor Credit Assessment: Inadequate credit risk assessment and poor lending practices can contribute to an increase in non-performing assets.
Sectoral Challenges: Specific industries facing downturns can impact the repayment capabilities of borrowers operating within those sectors.
Regulatory Changes: Changes in banking regulations, including stricter classification norms for NPLs, can lead to a higher reported NPL ratio.
Strategic Implications:
The rising NPL ratio poses several strategic challenges for NBL:
Profitability Impact: Higher NPLs necessitate increased provisioning, which can erode the bank’s profitability.
Capital Adequacy: Persistent high levels of NPLs can strain the bank’s capital adequacy, impacting its ability to lend.
Investor Confidence: A rising NPL ratio can adversely affect investor confidence, potentially leading to a decline in stock prices.
Recommended Actions for NBL:
To mitigate the growing NPL issue, NBL must adopt a multifaceted approach:
Strengthen Credit Risk Management: Enhance the credit risk assessment processes to ensure robust evaluation of borrowers' repayment capacities.
Aggressive Recovery Measures: Implement aggressive recovery and resolution strategies to manage existing NPLs.
Diversify Loan Portfolio: Diversify the loan portfolio to reduce exposure to high-risk sectors and borrowers.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure strict compliance with regulatory requirements to maintain transparency and accountability.
Conclusion:
The upward trend in NPLs at Nepal Bank Limited is a red flag that requires immediate and strategic intervention. By focusing on improving credit risk management, adopting rigorous recovery measures, and diversifying the loan portfolio, NBL can address the challenges posed by rising NPLs and safeguard its financial health. The bank's ability to manage its NPLs effectively will be crucial in maintaining investor confidence and ensuring long-term sustainability.
NBL's Net Worth per Share Shows Mixed Performance Over Five Years
Nepal Bank Limited (NBL) has reported mixed performance in its Net Worth per Share over the past five years. The latest data for the third quarter of the fiscal year 2080/2081 shows a slight increase to Rs. 246.42, compared to Rs. 241.97 in the same quarter last year. However, the bank's net worth per share has generally trended downward over the five-year period.
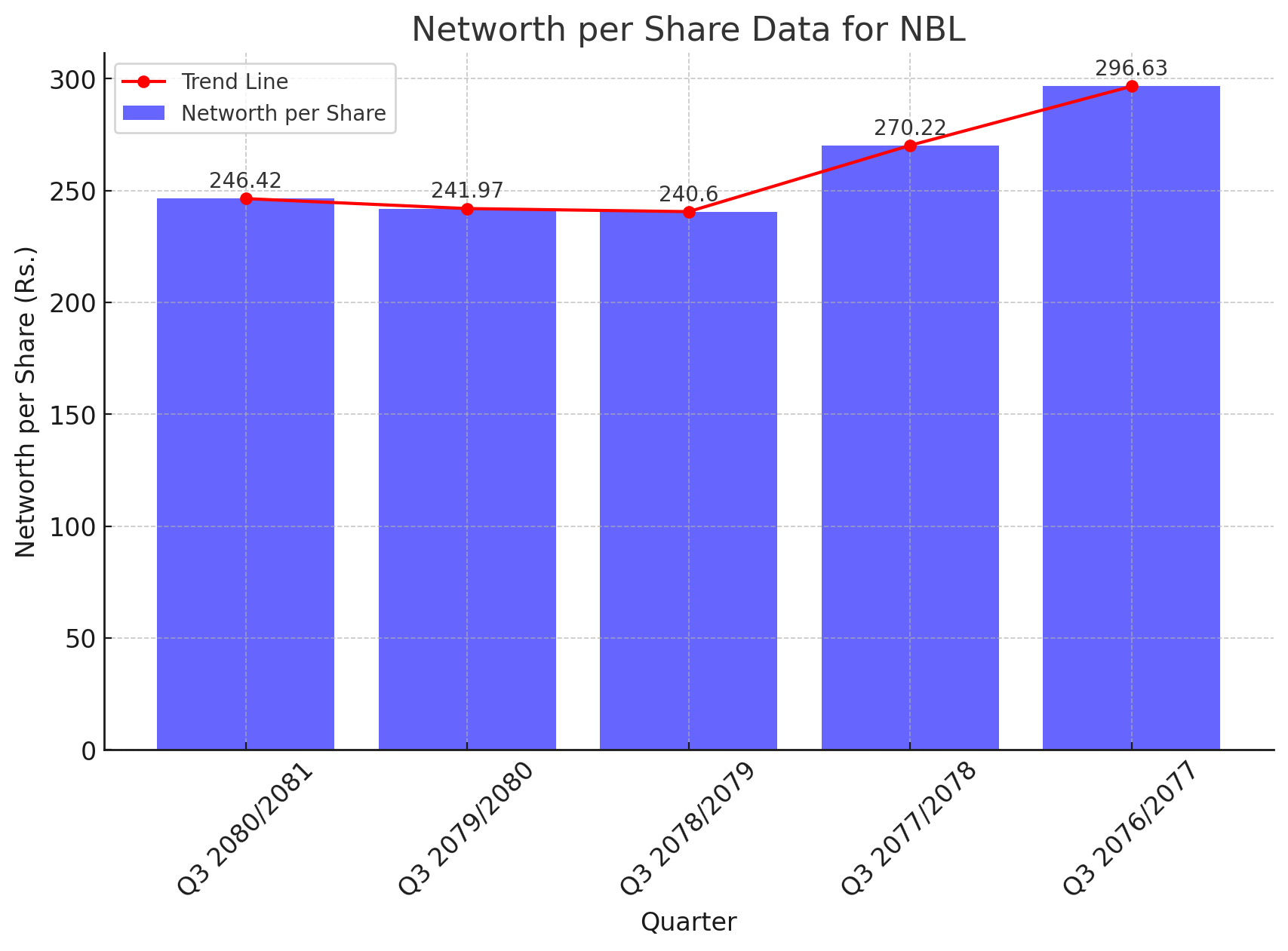
Historical Net Worth per Share:
Q3 2080/2081: Rs. 246.42
Q3 2079/2080: Rs. 241.97
Q3 2078/2079: Rs. 240.6
Q3 2077/2078: Rs. 270.22
Q3 2076/2077: Rs. 296.63
Interpretation:
The fluctuations in NBL's Net Worth per Share reflect the bank's ongoing challenges and efforts to stabilize its financial position. Several factors can be attributed to this trend:
Asset Quality Issues: The bank's rising non-performing loans have impacted its overall asset quality, affecting net worth.
Economic Conditions: Broader economic conditions and market volatility have influenced the bank's financial performance.
Capital Adequacy: NBL's efforts to maintain capital adequacy amidst regulatory changes and market pressures have contributed to the mixed performance.
Strategic Implications:
The mixed trend in Net Worth per Share highlights several strategic challenges and areas for improvement:
Strengthening Asset Quality: Addressing the rising NPLs is crucial to improving asset quality and enhancing net worth.
Capital Management: Efficient capital management strategies are necessary to maintain capital adequacy and support growth.
Operational Efficiency: Enhancing operational efficiency can help improve profitability and stabilize net worth.
Recommended Actions for NBL:
To address these challenges and enhance its financial position, NBL should consider the following strategic actions:
Enhance Risk Management: Implement robust risk management practices to mitigate asset quality issues and manage non-performing loans.
Focus on Profitability: Develop strategies to enhance profitability, including cost optimization and revenue diversification.
Capital Strengthening: Strengthen capital base through strategic capital raising initiatives and efficient capital allocation.
Operational Improvements: Improve operational efficiency through technological advancements and process optimization.
Conclusion:
The mixed performance in NBL's Net Worth per Share underscores the need for strategic interventions to stabilize and enhance its financial position. By focusing on asset quality, profitability, and operational efficiency, NBL can address its current challenges and achieve sustainable growth. The bank's ability to navigate these challenges will be crucial in maintaining investor confidence and ensuring long-term stability.
NBL's Return on Equity Hits a Record Low: A Deep Dive into the Declining Trend
Nepal Bank Limited (NBL) has reported a significant decline in its Return on Equity (ROE) over the past five years. The latest data for the third quarter of the fiscal year 2080/2081 shows an alarming drop to 0.48%, compared to 6.68% in the same quarter last year. This decline represents a broader trend of deteriorating financial performance for the bank.
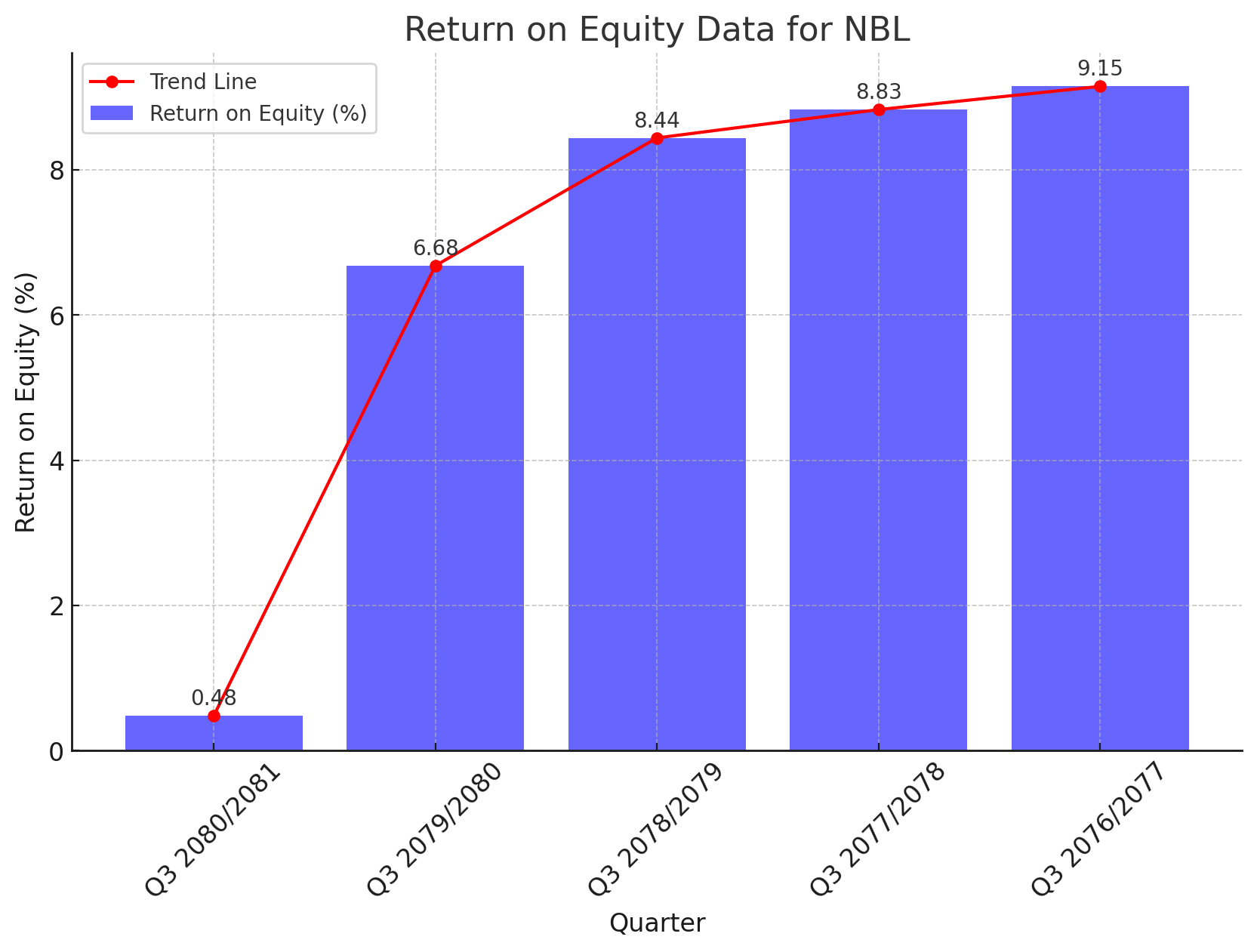
Historical Return on Equity (%):
Q3 2080/2081: 0.48%
Q3 2079/2080: 6.68%
Q3 2078/2079: 8.44%
Q3 2077/2078: 8.83%
Q3 2076/2077: 9.15%
Interpretation:
The sharp decline in ROE is a critical indicator of the bank's reduced profitability and efficiency in generating returns from its equity base. Several factors can be attributed to this trend:
Declining Profit Margins: Reduced earnings, as indicated by falling EPS, have directly impacted the bank's ability to generate returns on equity.
Rising Non-Performing Loans: The increase in NPLs has led to higher provisioning costs, eroding profitability.
Economic Slowdown: Broader economic challenges have affected the bank’s performance, reducing overall returns.
Operational Inefficiencies: Persistent operational challenges and increased costs have further squeezed profit margins.
Strategic Implications:
The declining ROE poses several strategic challenges for NBL:
Investor Confidence: A low ROE undermines investor confidence, potentially impacting stock prices and the bank's ability to raise capital.
Profitability Concerns: Sustained low profitability can affect the bank's long-term viability and growth prospects.
Operational Reforms: The need for significant operational reforms becomes evident to address inefficiencies and improve financial performance.
Recommended Actions for NBL:
To address the declining ROE and enhance its financial health, NBL should consider the following strategic actions:
Enhance Profitability: Implement strategies to boost earnings, such as expanding revenue streams and improving cost management.
Strengthen Risk Management: Focus on reducing NPLs through improved risk assessment and recovery strategies.
Operational Efficiency: Invest in technology and process optimization to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Capital Optimization: Optimize capital structure to ensure efficient use of equity and enhance returns.
Conclusion:
The significant decline in NBL's ROE is a red flag that necessitates immediate and strategic intervention. By focusing on improving profitability, strengthening risk management, and enhancing operational efficiency, NBL can address its current challenges and work towards restoring investor confidence and achieving sustainable growth. The bank's ability to implement these changes effectively will be crucial in reversing the declining trend and ensuring long-term stability and success
NBL's Distributable Profit per Share Takes a Sharp Dive: Analyzing the Decline
Nepal Bank Limited (NBL) has reported a concerning decline in its Distributable Profit per Share for the third quarter of the fiscal year 2080/2081. The latest data shows a negative figure of Rs. -7.12, a stark contrast to Rs. 1.23 reported in the same quarter last year. This marks a significant downturn in the bank's profitability.
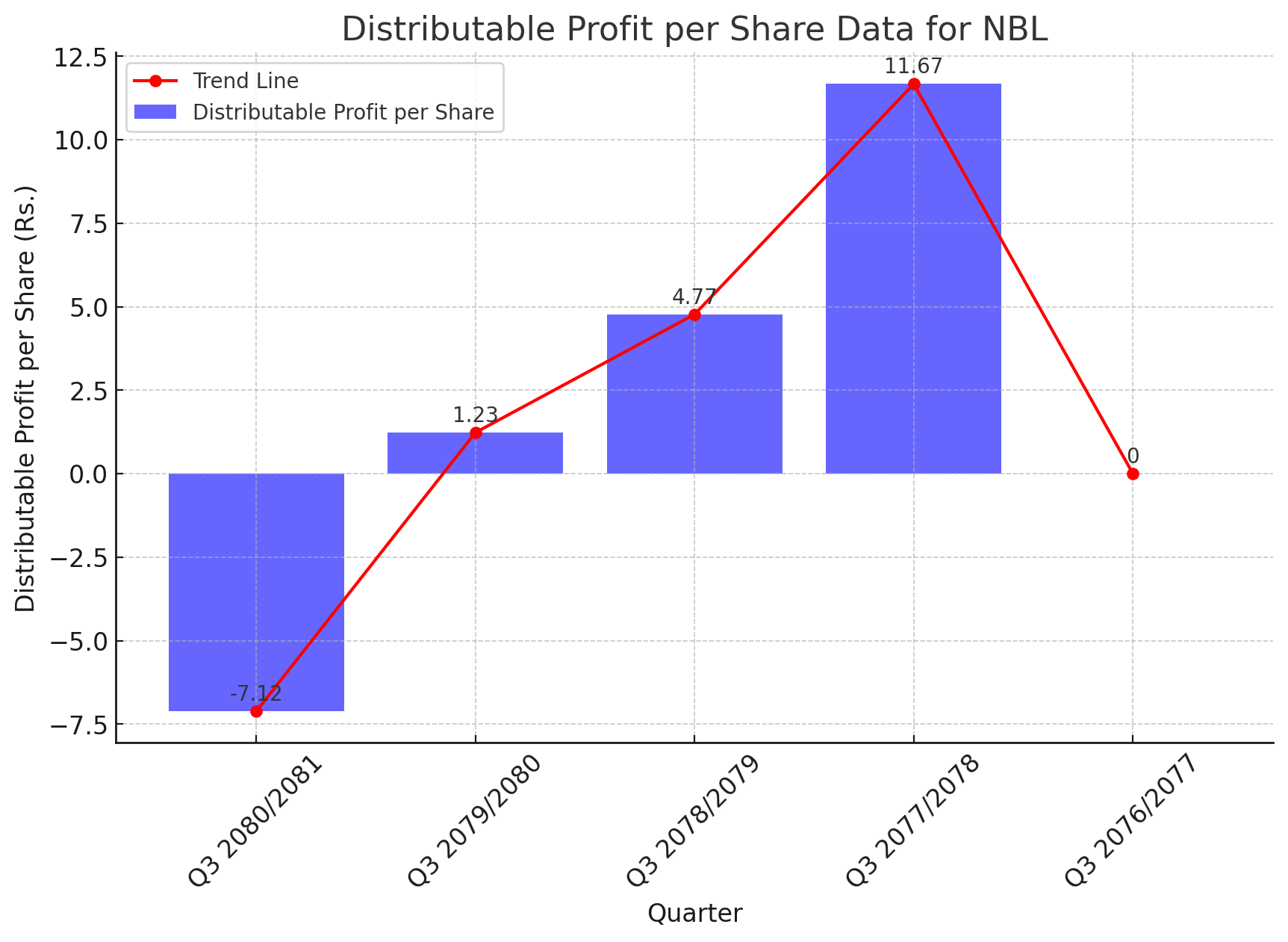
Historical Distributable Profit per Share:
Q3 2080/2081: Rs. -7.12
Q3 2079/2080: Rs. 1.23
Q3 2078/2079: Rs. 4.77
Q3 2077/2078: Rs. 11.67
Q3 2076/2077: Rs. 0
Interpretation:
The drastic decline in distributable profit per share indicates severe financial stress and challenges within NBL. Several factors can be attributed to this trend:
Operational Losses: The negative figure suggests significant operational losses, which may be due to increased expenses or reduced revenue.
High Provisions: Increased provisions for non-performing loans (NPLs) could have eroded the profits, impacting distributable earnings.
Economic Impact: Broader economic challenges, such as reduced economic activity and financial market volatility, have likely contributed to the downturn.
Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulatory requirements may have necessitated higher reserves or impacted profitability.
Strategic Implications:
The negative distributable profit per share has several strategic implications for NBL:
Investor Confidence: Negative profits erode investor confidence, potentially leading to reduced investments and a decline in stock prices.
Dividend Distribution: The negative distributable profit directly impacts the bank's ability to distribute dividends to shareholders.
Financial Health: Sustained financial losses threaten the bank’s long-term viability and stability.
Recommended Actions for NBL:
To address the declining profitability and improve financial health, NBL should consider the following strategic actions:
Cost Management: Implement stringent cost management measures to reduce operational expenses and improve profitability.
Strengthen Loan Recovery: Focus on improving loan recovery processes to reduce the burden of NPLs and enhance financial stability.
Revenue Diversification: Explore new revenue streams and diversify income sources to mitigate the impact of economic challenges.
Operational Efficiency: Invest in technology and process optimization to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Conclusion:
The significant decline in NBL's distributable profit per share highlights the urgent need for strategic intervention. By focusing on cost management, loan recovery, revenue diversification, and operational efficiency, NBL can work towards reversing the downward trend and restoring financial stability. The bank's ability to navigate these challenges effectively will be crucial in rebuilding investor confidence and ensuring sustainable growth in the future.









