By Sandeep Chaudhary
Nepal's Foreign Trade Analysis: A Deep Dive into Historical Trends and Implications

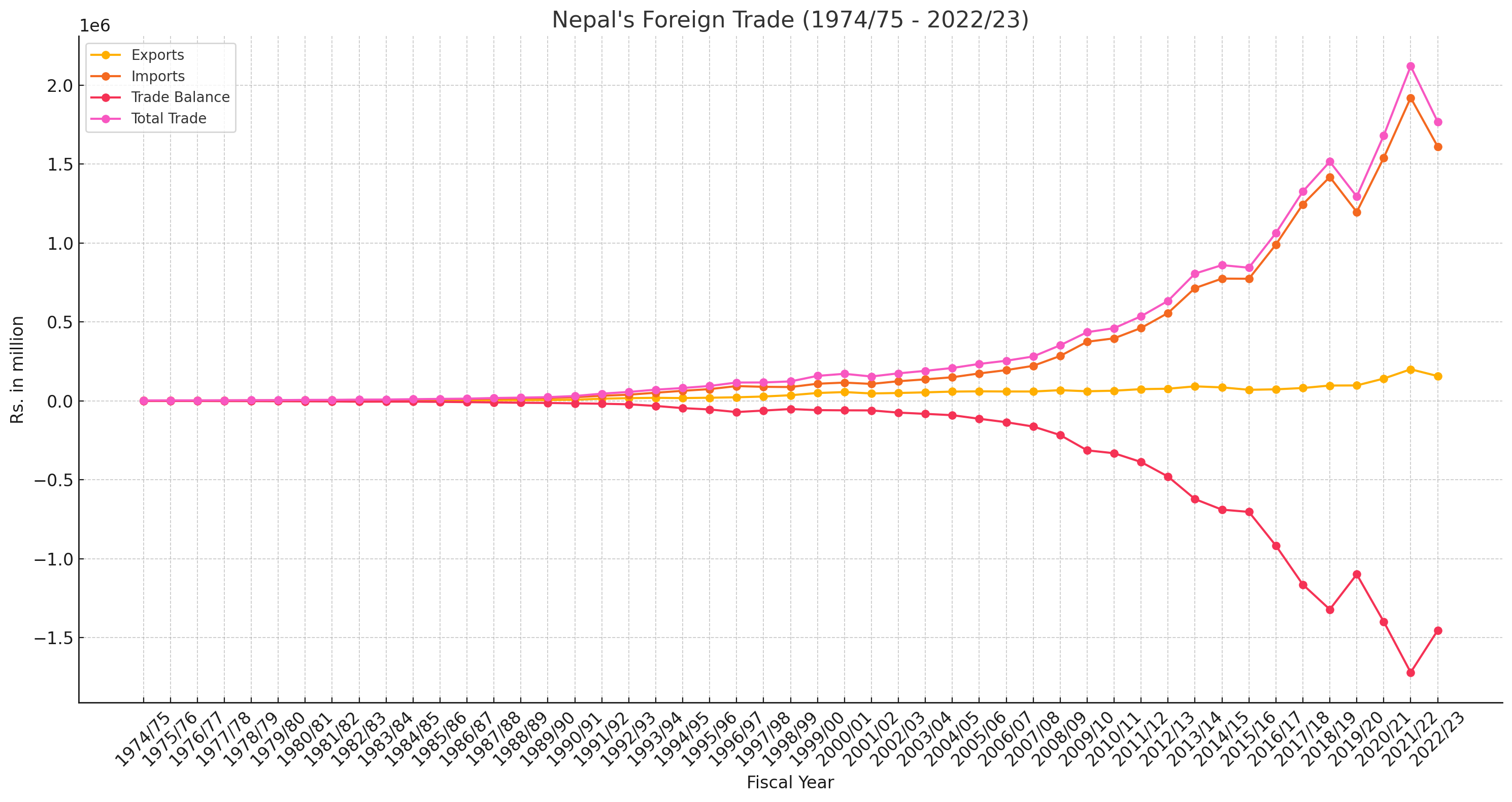
Nepal's foreign trade landscape has witnessed significant fluctuations over the past five decades, reflecting both internal economic policies and external global market dynamics. The data from the fiscal year 1974/75 to 2022/23 provides an insightful view of the trends in exports, imports, trade balance, and total trade, offering a comprehensive understanding of the country's economic trajectory.
Key Trends and Observations:
Increasing Trade Volume:
Over the years, there has been a substantial increase in the total trade volume. From Rs. 2,704.2 million in 1974/75 to Rs. 2,120,479.3 million in 2021/22, the trade volume has expanded tremendously. This growth indicates Nepal's increasing engagement with global markets.
The sharp rise in total trade in recent years, particularly noticeable from the 1990s onward, underscores the country's efforts to integrate more deeply into the global economy.
Persistent Trade Deficit:
Throughout the entire period, Nepal has consistently experienced a trade deficit, where imports far exceed exports. The trade deficit has widened from Rs. 925.0 million in 1974/75 to a staggering Rs. 1,720,417.4 million in 2021/22.
The widening trade deficit is a critical concern, indicating a heavy reliance on imports and insufficient export growth to balance the trade.
Fluctuating Export and Import Growth Rates:
Export growth has seen significant fluctuations, with periods of high growth, such as 1984/85 (60.8%) and 1991/92 (85.5%), contrasted with years of decline, such as 1981/82 (-7.3%) and 2001/02 (-15.6%).
Import growth has generally remained high, particularly in the 1990s and 2000s, indicating an increasing demand for foreign goods and services. However, there were periods of slower growth or decline, such as 1997/98 (-4.9%) and 2022/23 (-16.1%).
Impact of Global and Domestic Factors:
Various global economic events and domestic policies have impacted trade figures. For instance, the global financial crisis of 2008/09 and the subsequent economic slowdown saw a reduction in import growth and a notable decline in the trade balance.
Domestic factors such as political instability, infrastructural challenges, and economic policies have also played a significant role in shaping trade dynamics.
As Percent of GDP:
The data indicates a steady increase in trade as a percentage of GDP, reflecting the growing importance of foreign trade in the national economy. However, the increasing trade deficit as a percentage of GDP also signals potential vulnerabilities, particularly in terms of foreign exchange reserves and economic stability.
Interpretation and Implications:
Economic Diversification and Export Promotion: The persistent trade deficit highlights the urgent need for Nepal to diversify its economy and promote exports. There is a critical need to develop export-oriented industries, improve product quality, and explore new markets. Strengthening sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism can boost export earnings.
Import Substitution: Reducing reliance on imports through the development of local industries is essential. Policies aimed at import substitution, coupled with incentives for local production, can help mitigate the trade deficit.
Policy Interventions: Strategic policy interventions are necessary to balance trade. This includes negotiating favorable trade agreements, improving trade logistics and infrastructure, and implementing measures to enhance the competitiveness of Nepali products in international markets.
Sustainable Economic Growth: Ensuring sustainable economic growth requires a balanced approach to trade. While engaging with global markets is crucial, maintaining a healthy trade balance is equally important to avoid long-term economic challenges.
In conclusion, Nepal's foreign trade data over the years paints a picture of significant growth and challenges. Addressing the trade deficit, promoting exports, and adopting sustainable economic policies are pivotal for ensuring the country's economic resilience and growth in the global arena.









